First, what is AI?
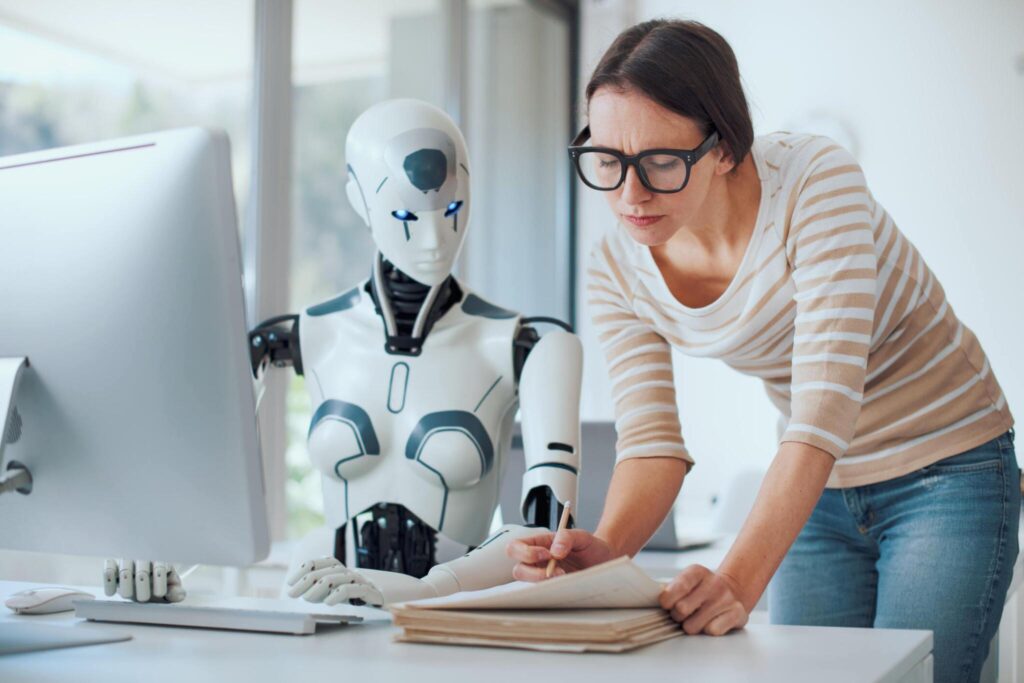
Simply stated in simple terms, AI, also known as artificial intelligence (AI) can be described as the imitation of human intelligence functions through machines, specifically computers. The objectives of AI include enhanced learning through computers as well as reasoning and perception. Particular application areas that make use of AI are expert systems and natural language processing speech recognition, and machine vision. AI is used in a variety of industries, from healthcare to finance.
A QUICK HISTORY
- Automation started in the Industrial Revolution and machinery from 1790 to 1840. In the past, as now people were concerned about the effects that automation would have on their work. But Industrial revolutions actually led to job opportunities.
- From 1837 onwards, Charles Babbage started the development of a machine that he named “The Analytical Engine,” now referred to by the name of computer.
- Take a leap forward towards the early 1990s which was a period that saw major advancements in AI. A computer-generated intelligence known as ‘ Deep Blue beat the world’s top chess player Garry Kasparov at chess. NASA has launched the first robotics robot, Sojourner located to the planet of Mars. Then AI-based data extraction software became an integral part of the wide-spread use of web. The 90’s were also the time when automation was integrated and business processes management.
- The launch of Siri by Apple Siri led to a new era of AI-driven automation and assistants. AI has moved away from mechanical robots and into the advancement of automated automation. Business Process Automation (BPA) was getting more efficient and refined.
- Nowadays automation software is now an absolute necessity, not an option. It’s not perfect, but it’s growing and improving each day.
Jobs at Risk
Here’s a list of 10 jobs that may be taken over in the near future by AI soon.
1. ENTRY-LEVEL ADMIN ROLES
Administrative and office support is identified as the position that has the highest percentage (46 percent) of the current tasks that could be automated and executed by AI. This could result in an important change in office workflow and will require upgrading the skills of many administrative positions.
2. DATA ENTRY CLERKS
Jobs that require decision-making based on data analysis, such as financial analysis and medical diagnosis” are the most at risk, according the Angelo Sorbello, CEO of AI SEO and writing tool Linkdelta. “In general, any job that involves performing a set of predefined steps or following a strict set of rules is vulnerable to automation,” the CEO said.
3. SOFTWARE ENGINEERS & CODERS
AI can automatize a lot of the routine testing engineers are currently performing in the course of development, as well being able to find issues and patches.
4. CUSTOMER SERVICE REPRESENTATIVES
Businesses are employing AI to handle customer service inquiries Many small-sized businesses aren’t able to have human employees in these jobs, so it’s now becoming commonplace. Jonathan Tian, CEO of CreditYelp states it is because AI “has taken over the customer support response” within the company. “Most frequently queried responses are fed to the algorithm to assist our online clients with immediate replies” Tian added.
5. LEGAL ASSISTANTS
AI Legal assistants have commercially available. They review documents, legal research memos and aid lawyers with deposition preparation. They’ll also analyze contracts and modify them in case they violate regulations on compliance, as to identify any threats your company could face.
6. COPYWRITING & CONTENT PRODUCTION
ChatGPT can create efficient paragraphs of relevant pertinent content in a matter of minutes – much like editors or writers can, but faster. ChatGPT, Jasper and Writesonic are all established in the AI world, and are charging high monthly fees for these premium offerings.
7. GRAPHIC DESIGNERS
AI tools such as DALL-E can create images in a matter of seconds which are quite comparable to those created by graphic designers. If technology can create exclusive, distinctive high-quality images today can do that now, what will it be able of doing within a year?
8. STOCK TRADERS
With its predictive analysis and real-time data processing, AI can potentially automate and improve trading strategies and challenge the traditional role of stock brokers. “I definitely think it will impact the trading side…people are hired out of college and spend two, three years to work like robots and do Excel modeling — you can get AI to do that in seconds,” according to Pengcheng Shi, Professor of Computing and Information Sciences at the Rochester Institute of Technology.
9. BANKERS & ACCOUNTANTS
AI’s ability to handle complex financial tasks could be far beyond human capabilities, making routine calculations unnecessary and leading accountants and bankers to more advisory capabilities.
10. FACT-CHECKERS & PROOFREADERS
In the event that Bard or ChatGPT gets some tweaks and gives sources for every answer it gives it could be an extremely accurate, real-time fact-checker. Reading large text which could take an experienced proofreader many hours to verify could now be checked for errors by AI programs in mere seconds.
The Impact of AI
The threat of losing jobs because of automation isn’t something new. In the past, every technological advance has usually created greater jobs that it has eliminated. If automation can make certain tasks more efficient, the human experience is often transferred to areas that are not yet covered by machines. But relying on the past for a guide may not be accurate. Today’s game changer is AI is a force that isn’t limited to one area but affects a variety of industries because of its abilities in processing language, patterns recognition and problem solving. Furthermore, the speed of technological advancement isn’t linear anymore and is growing exponentially.
In the current landscape the roles of robotics, programming and engineering are growing. But there’s a problem people who have been working in middle-skilled positions may be unable to make the transition without extensive education and training. Equally, the chances in the low-skilled sector could slow down as the spending capabilities of the middle-class decrease. Unaddressed, we’re at the edge of an increase in unemployment and its social repercussions. Less volunteerism as well as higher rates of crime and addiction to drugs are all connected.
The solution? A major overhaul of our educational system, removing obsolete industrial-age models. In the AI age, fundamental skills are changing and education isn’t only a once-in-a-lifetime experience. Re-learning and continuous learning needs to become the norm, while adjusting to the rapid rate of digital transformation.
Despite this however, there’s a chance. Machines, even though they surpass us in a variety of tasks, aren’t equipped with the human touch. They cannot comprehend our wishes or map our goals. Humans will always be able to play the privilege of seeing the future, and working with machines to realize it to ensure our importance in the tapestry of the future.
Adapting to Change
A wide range of skills is essential for the creation and implementation for AI systems. Expertise in programming in a range of languages, along with proficiency with development tools and frameworks are required for AI specialists. The jobs that are expected to be in high demand today and in the coming years include:
1. MACHINE LEARNING ENGINEER
A highly sought-after positions in AI engineers, they must be skilled in the field of software and be able to use predictive models and use natural language processing when working with huge data sets. They should be familiar with methodologies for software development including agile methods, agile techniques, as well as a variety of the latest software development tools.
2. ROBOTIC SCIENTIST
Their main function is to design and build mechanical machines or robots capable of performing tasks using instructions from humans. Other skills that are required for this job include the writing and manipulation of computer programs, working with other experts and constructing prototypes.
3. DATA SCIENTIST
Data scientists analyze, collect and interpret large quantities of data using algorithms for machine learning as well as predictive analytics in order to get insights that go beyond statistical analysis. They must be proficient in the use of Big Data platforms and tools.
4. RESEARCH SCIENTIST
Research scientists are expert in many areas, such as computational statistics, machine learning as well as applied math.
5. BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE DEVELOPER
To analyze complicated data and find recent trends in the market and business They must be skilled in both analytical and technical abilities, as well as have solid communications and problem-solving capabilities. They are accountable for conceiving and constructing, modeling and maintaining information for the complex, extensive and accessible cloud-based platforms for data.
6. AI PRODUCT MANAGER
To ensure you are sure that AI solutions and products meet requirements of the client and corporate objectives To ensure that AI products and services meet client demands, An AI product manager collaborates with teams from across the functional spectrum, which includes data scientists, software developers and business stakeholder.
7. ROBOTICS ENGINEER
An expert who designs the, designs, and manages robotics and robots usually conducts market research as well as customer needs analysis, then design and build robotic systems that meet these requirements, analyze and troubleshoot the system, and continuously improve the system’s performance.
8. NLP ENGINEER
A person who develops models and formulas to aid computers in understanding the language, understand, and generate human language is called an NLP (Natural Language Processing) engineer. An NLP engineer’s job usually consists of researching and the implementation of NLP techniques into use as well as developing and improving NLP models and the integration of NLP techniques into software programs.
9. RESEARCH ASSISTANT
Research assistants are typically responsible for collecting and analyzing data, evaluating new algorithms, and assisting to develop apps that make use of AI.
10.DEEP LEARNING ENGINEER
A deep-learning engineer is an expert in developing and constructing deep neural networks which can absorb vast amount of data.
Policy & Ethical Considerations
With the advent of rapidly evolving AI We are on the nexus of a revolutionary technological advancement. AI with its unparalleled ability, presents opportunities as well as challenges. In order to ensure that workers can adapt and reap the rewards of automation is not simply acknowledgment, but the right action and the comprehensive response of the policy is crucial.
To guide this change to a more efficient and effective AI, in the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy has defined five fundamental principles that guide AI’s integration into society ethically. The most important is the development of “Safe and Effective Systems” which includes testing prior to deployment that assures the safety of the public. Equally important is battling “Algorithmic Discrimination,” which requires a constant and constant commitment to fair design of systems. The most important aspect of protecting individual rights are “Data Privacy” and the right to access. “Notice and Explanation” adds to this, claiming that each citizen has the right to be aware of and be aware of how automated systems impact their lives. In addition, the principle that underlies “Human Alternatives” stresses the importance of personal intervention, allowing individuals to option to opt out and assistance from a human.
The ethical concerns associated with AI’s explosive rise are numerous. The potential for AI to reveal private information is a major privacy hazard. As we move forward in the direction of AI integration the complexity of criminal and civil responsibility become crucial, with AI’s actions around the globe posing questions about accountability and accountability.
Furthermore, AI’s influence reaches deeper social veins, impacting the way people work, taxation as well as the political system. It is challenging traditional norms of labor which could change the nature of jobs and income patterns. The tax implications, as well significant; AI’s efficiency could alter the focus of fiscal policy, which could have negative impacts. In addition, the impact of AI on political debates is too important to ignore regardless of whether bots are influencing the narratives of politicians or enhancing transparency. The road ahead in the direction of the development or regulation, requires an equilibrium, accepting the potential of AI while preserving the fundamental ethical and democratic principles.
Conclusion
Generative AI is perhaps the most revolutionary technology we have invented in a lengthy period of time. It’s also an extremely efficient tool for companies and businesses, which is a significant source of creating new ideas or breakthroughs. However, it is important to think about the possibility that AI could also be used to harm us and create maximum harm in a wide range of areas in our lives. It all depends on the intention of the creators of how they wish to utilize AI.
It is important to address the following issues What can be done to ensure that AI encourages fairness and diversity? What can we do to help the regulatory system improve without hindering responsible technological innovation? What can we do to safeguard security and privacy? Are there ways to help AI help to boost innovation and growth? What kind of workforce will the future appear like? What can we do to help America ensure that the United States remain competitive and be the leader in AI? The future of AI will be determined by the decisions taken regarding AI.
My top advice for staying afloat in these changes? Be in good health. Be updated. Be flexible.