On-page SEO is the process of optimizing various front-end and back-end components of your website so that it ranks in search engines and brings in new traffic. Just creating and publishing your website isn’t enough. You need to optimize it for Google in order to rank and attract new traffic. It’s called “on-page” SEO because the tweaks and changes you make to optimize your website can be seen by visitors on your page, whereas off-page and technical SEO elements aren’t always visible. Every part of on-page SEO is completely up to you; that’s why it’s critical that you do it correctly.(Content Optimization)
On-page SEO is important for both search engines and people. It helps search engines understand your website and its content. Google is increasingly focused on relevance in order to better understand what users are actually searching for when they type a query and deliver results that meet user intent.
Google’s “How Search Works” Report

“The most basic signal that information is relevant is when a webpage contains the same keywords as your search query. If those keywords appear on the page, or if they appear in the headings or body of the text, the information is more likely to be relevant.” Source: Google’s “How Search Works” report
This means you need to be selective with the keywords you use.
While it might be tempting to use a lot of keywords on your pages in hopes of matching as many queries as possible, this won’t help you rank. You need to think about what would be helpful to people searching and create content to answer their questions. Focus your efforts on optimizing for just one keyword or key phrase per page. In this video, we’ll cover the basics of optimizing your content for search engines. This is the foundation for creating search-friendly content (Content Optimization). There are many more aspects of on-page SEO to consider as well, which you can learn about in the resources section.
we’re going to cover these elements of on-page SEO:
- Heading tags
- Title tags
- External links
What is a page heading tag?
An HTML element that provides a hierarchical structure to a web page. In the early days of search engines, heading tags were direct ranking factors. Today, headings don’t directly impact your SEO. However, they do have indirect benefits. Well-written headings make your page easier to read and navigate. This creates a better experience for the user and helps your SEO. If your page lacks structure and visitors can’t find what they need, they’ll leave your site and search for their answer somewhere else. This increases your bounce rate, which search engines pay attention to. Just like most aspects of SEO, always put your users first. Use headings to add structure to your content (Content Optimization). Describe what each section is about so that visitors can quickly find what they’re looking for.
Best Practices for Page Headings
- Your page title should have an H1 tag.
- Subsequent headings on the page should have an H2 or H3 tag, and so on
- Use your primary keyword in your page title.
First, you’re limited to one H1 heading per page.
This should be your page’s name. Think of the H1 heading like the name of a book. Some CMS platforms will tag your title automatically, but it’s a good idea to make sure your page heading is an H1. As you continue down the page, use H2 or H3 headings to break out different sections. Heading tags have levels corresponding to their importance on the page. An H1 is more important than an H2, which is more important than an H3, and so on. Search engine crawlers use these tags to scan through your content, so make sure that your section headings use this format. It’s unlikely that you’ll need to go any further than an H3, but if you’re writing a very long piece of content with many sub-categories, you can use subsequent tags.
Here’s an example of how heading tags appear on a blog post.
H1: A Quick Primer on Google’s Search Engine Results Page (SERP)
H2: What Does SERP Stand For?
H2: SERP Features
H3: Rich Snippets
H3: Paid Results
H3: Universal Results
Finally, make sure you include your target keyword in your page heading.
This is less about having your heading exactly match the keywordand more about accurately describing your page’s contents (Content Optimization). For example, if you’re writing a blog post about the top 10 cities to live in North America, a good heading for that post could be, “The Top 10 Cities to Live in North America.” If you’re a wedding planner creating your website’s services page, the heading of that page might be, “Wedding Planning Services.”
What is a title tag?
An HTML element that specifies a web page’s title (also known as the “SEO title”). The title tag and the heading tag are two different things, but they’re often written in the same way. Your heading tag is meant for people who are already on your site to tell them what a given page is about. Your title tag, on the other hand, is meant for people who aren’t yet on your website. It’s what displayed in the search engine results pages (or SERPs), and its purpose is to entice people to click through onto your website. In most CMSes, the title tag defaults to match the page heading, and often, this is fine. If you’ve written an effective page heading that accurately describes your page’s contents (Content Optimization), this will usually function just as well in search engines.
This title in SERPs is the same as the page heading.
Sometimes, it helps to have a different title tag than your heading tag.
For instance, if your page heading is very long, it may benefit you to write a shorter version for your title. This is
because after a certain number of characters (about 60), your title will get cut off in Google. Let’s look at this
example.
This title tag is too long. It gets cut off in search engine results, so searchers can’t read the entire thing.
Pro Tip: Preview Your Title Before Publishing
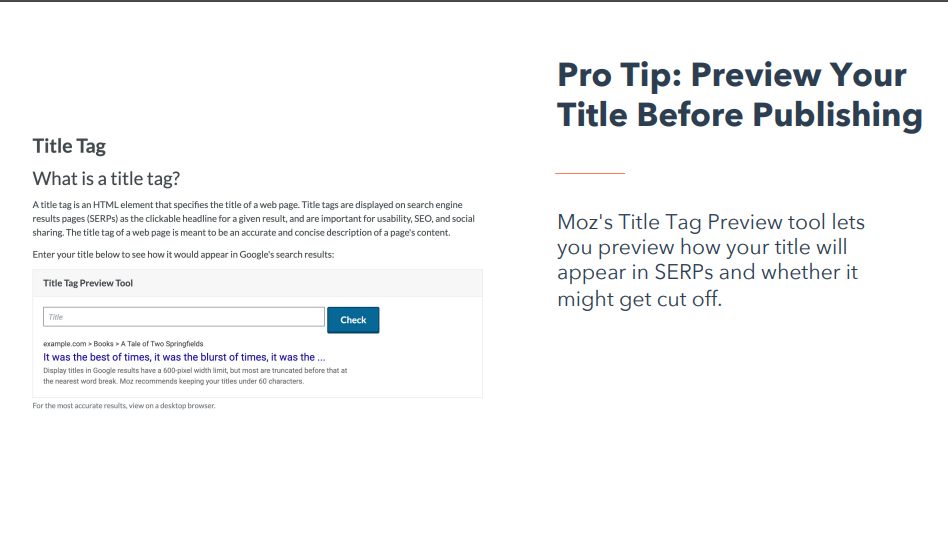
Moz’s Title Tag Preview tool lets you preview how your title will appear in SERPs and whether it might get cut off. Best Practices for Title Tags
Include your primary keyword in your title tag.
- Keep your title under 60 characters, if possible.
- Make sure both your page heading and title answer the searcher’s primary question.
- It also helps your on-page SEO to include external links on your pages.
These are links to other website’s content (Content Optimization). If you link to authoritative websites to support your claims, this can help your site’s SEO. Just like you might not trust a paper or a news story that didn’t cite any sources, when you link to quality external content (Content Optimization), it shows your readers and search engines that you’ve done your research. You should write first and foremost for your readers, and to be informative and trustworthy, you need to link to your sources.Tools to Help Optimize Your Content