What is a URL?

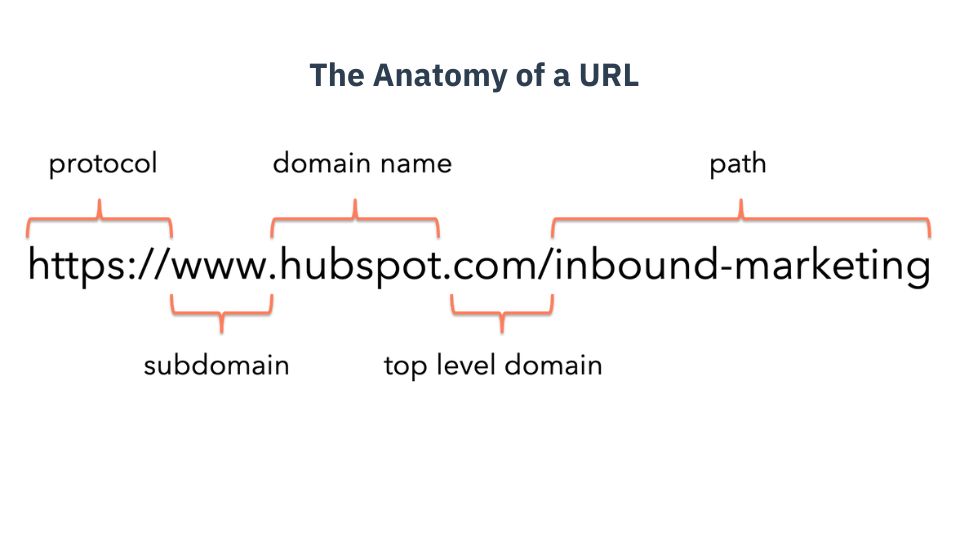
The URL (Uniform Resource Locator) specifies the whereabouts of a web-based resource. It is akin to an address. Like you can locate the address of a building, it is possible to discover a website online through its URL. URLs were created to replace IP addresses. These are large strings of numbers used by computers to connect with servers. It makes the web more convenient to navigate for human beings. It is the Anatomy of a URL
What do the URL’s elements have to do with it?
First, there is the protocol. The protocol specifies the way a browser can retrieve information from a web page. The protocol of choice has “http” as well as “https” (the S stands for “secure”). You may also have come across “mailto:” which opens the user’s default email client. The next step after this, the user will be able to access the subdomain. It helps arrange different sections on your site. There isn’t always a need for an additional domain, but it depends on the features of your CMS and the structure of your website. The most common domain is “www.” It is possible to see subdomains that include “blog” as well as “store” and “help” However, the subdomain could be nearly everything. For instance,
the Nexorank Academy website lives on the subdomain “academy” so its URL is “academy.Nexorank.com.” Following your subdomain (if you already have the one) it is most crucial element of the URL: the domain’s name.
It’s the human-readable representation of the location of a website’s in the Internet. Your domain name must be identical to your company’s name if managing a website for business. Therefore, Nexorank’s domain will be “Nexorank.” Your domain name is yours to your site, but it should be a description of the contents of your website. Be aware that you must purchase an domain name through a registrar therefore you will be restricted by what domain names are available. The second part that makes up the domain name is top-level domain, also known as TLD. The suffix is in the middle of your domain’s name. The most popular is “.com” however you’ll also see numerous other suffixes that include “.net,” “.org,” “.edu,” and others. Domain name as well as the top-level domain make up”the root domain. The last element of a URL is called the path. This is the place where an asset, for instance an article, a blog post or file, is kept on a site. It may also contain the organizational aspects of your website such as subfolders and dates. Some URLs do not include an associated path. The homepage of your website is an instance that does not have one.
The Effect Of URLs On SEO
URLs impact your SEO in a variety of ways:
- They enhance your user’s experience.
- They’re a factor that determines ranking in search engines.
- They assist search engines and users understand what you are trying to convey with your content.
Best Methods to Write URLs - Include your principal keyword.
- Use hyphens between words.
- Keep them brief and simple.
- Write down the contents of the page.
- Make sure they’re informative.
- Include your desired keyword within your website’s URL.
It’s not a must however it’s a good idea to adhere to if you’re able. It’s less about stuffed keywords everywhere they move but more about proving that your site is devoted to an area of interest and communicating this to users and search engines. For instance, if have a website about the top homemade dog foods, it’s always a great idea to include “organic,” “dog,” and “treats” in your URL. This will make your site get noticed by search engines.
Search engine results since the results accurately reflect what users are going to see when they land on your website.
Use hyphens between words in your URL.
When writing your URLs, use hyphens between words. This is more efficient than writing a an unintelligible, long sequence of words, or using underscores. Also, refrain from using spaces inside your URL because they translate to three characters (%20) as well. This additional length can eventually result in your link breaking. Google’s developer manual specifically suggests using hyphens in between words, which is a recommendation you should to adhere to. The majority of
CMSes currently default their URL structure to incorporate the word separators hyphens. However, if yours doesn’t then make sure you include them in the URL prior to publishing your webpage.
Make your URLs as short as possible and easy.
This advice is straight from Google and Google. The more easily understood words are better than endless string of numbers. The trick is to make your URL simple and easy for humans and for search engines to comprehend. A URL that is shorter makes it simpler to share with users on social media.
Last but not least, ensure that your URL identifies the page visitors are expected to land on.
This is in line with the idea of the use of words in the URL. Through reading a URL the user and a engine will be able to get an idea of the content on the page. Making URLs can be a delicate act of making them informative and also ensuring that they’re clear. For more tips on creating search-friendly URLs, click here.